Xiaoyan Cao
 Ph.D. student Peking University
Ph.D. student Peking University
I am currently a Ph.D. student at Peking University (PKU), under the supervision of Prof. Huapeng Qin. Additionally, I am a remote visiting scholar at the University of Edinburgh, working with a Fellow of the Royal Academy of Engineering Prof. Alistair Borthwick. Previously, I obtained my M.S. degree from Xiamen University, where I was advised by Prof. Xiaoyu Cao, a recipient of the Excellent Young Scientists Fund (EYSF), and Prof. Shihui Guo. During my master's studies, I spent a year as an Algorithm Researcher (Intern) at Tencent AI Lab and was rated as an Outstanding Intern, under the joint supervision of Senior Engineer Dr. Lanqing Li and Expert Engineer Dr. Dijun Luo. I have closely collaborated with Dr. Yao Yao from Tsinghua University and Prof. Guangtao Fu from the University of Exeter.
My research mainly focuses on AI for Science, including AI applications in 2D hydrological and hydrodynamic simulations, multi-insect tracking, and greenhouse crop simulations. I am dedicated to exploring how to integrate domain knowledge into AI models, aiming to enhance generalization and produce results that are more aligned with physical laws. Recently, my focus has been on embedding hydrodynamic knowledge (e.g., shallow water equations) into neural networks to enable general flood modeling, including solving, generalization, and knowledge discovery.
My research has been published in multiple top-tier journals and conferences, such as IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, Pattern Recognition, Journal of Hydrology, AAAI, and ICAPS.

Experience
-

Tencent AI Lab
Algorithm Researcher (Intern) Mar. 2020 - Mar. 2021
Service
- Reviewer of IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics
- Reviewer of AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence
- Reviewer of Smart Agriculture Technology
News
Selected Publications (view all )

Segmentation of green roofs in high-resolution remote sensing images with GR-Net
Wang Zhi†, Xiaoyan Cao†, Yao Yao, Lian Feng, Huapeng Qin*(*corresponding author, †equal contribution)
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing (TGRS) 2025 SCI Q1
Accurately recognizing the spatial distribution of green roofs is crucial for quantitatively assessing their ecological benefits in urban areas. Deep learning has been applied to this task using remote sensing images, reducing time and labor costs. However, challenges remain due to the irregular shapes, sparse distribution, homogeneity with ground vegetation, and

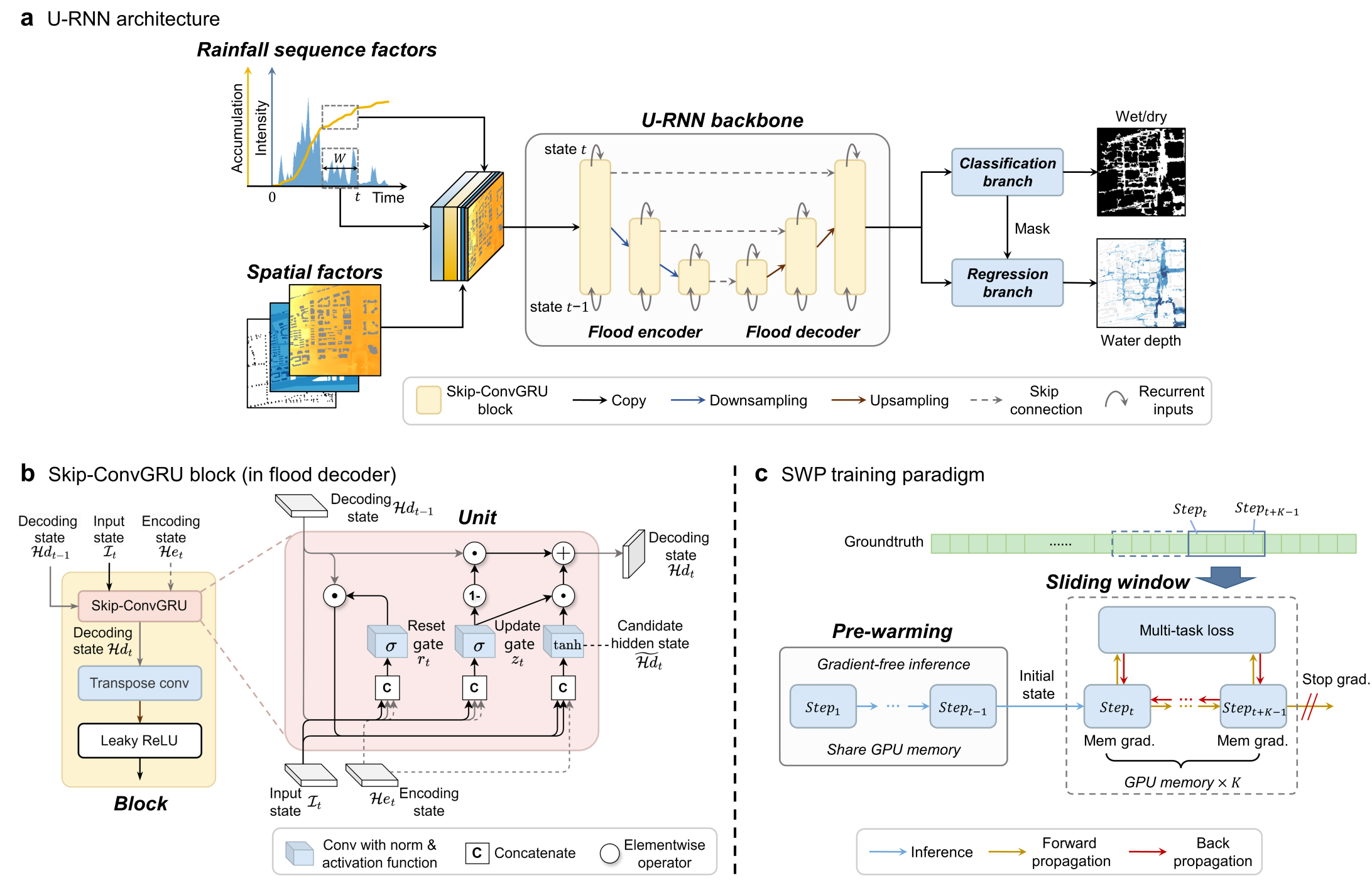
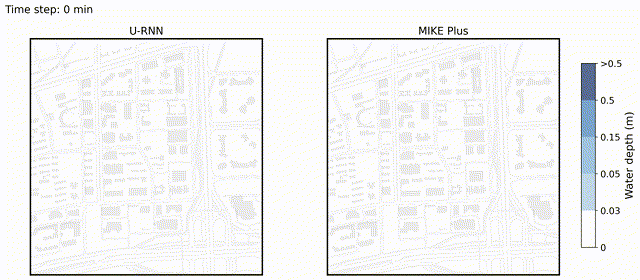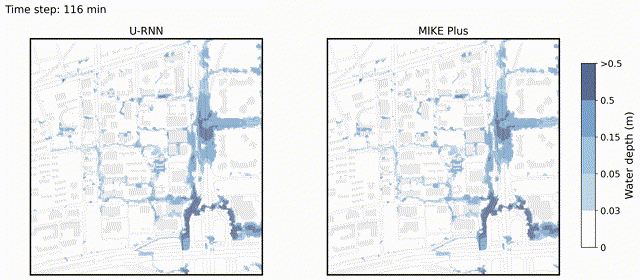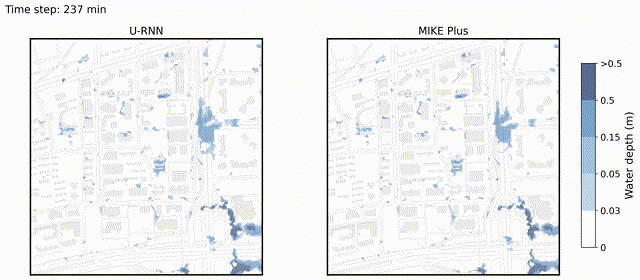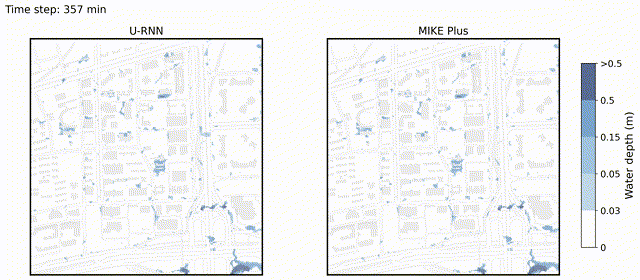
U-RNN high-resolution spatiotemporal nowcasting of urban flooding
Xiaoyan Cao, Baoying Wang, Yao Yao, Lin Zhang, Yanwen Xing, Junqi Mao, Runqiao Zhang, Guangtao Fu, Alistair GL Borthwick, Huapeng Qin*(*corresponding author, †equal contribution)
Journal of Hydrology (JoH) 2025 SCI Q1
We propose U-like Recurrent Neural Network (U-RNN), a latent autoregressive architecture, to represent the spatiotemporal dynamic process of urban flooding, and a Sliding Window-based Pre-warming (SWP) training paradigm to reduce computational demand and enhance the generalization of full sequence predictions.


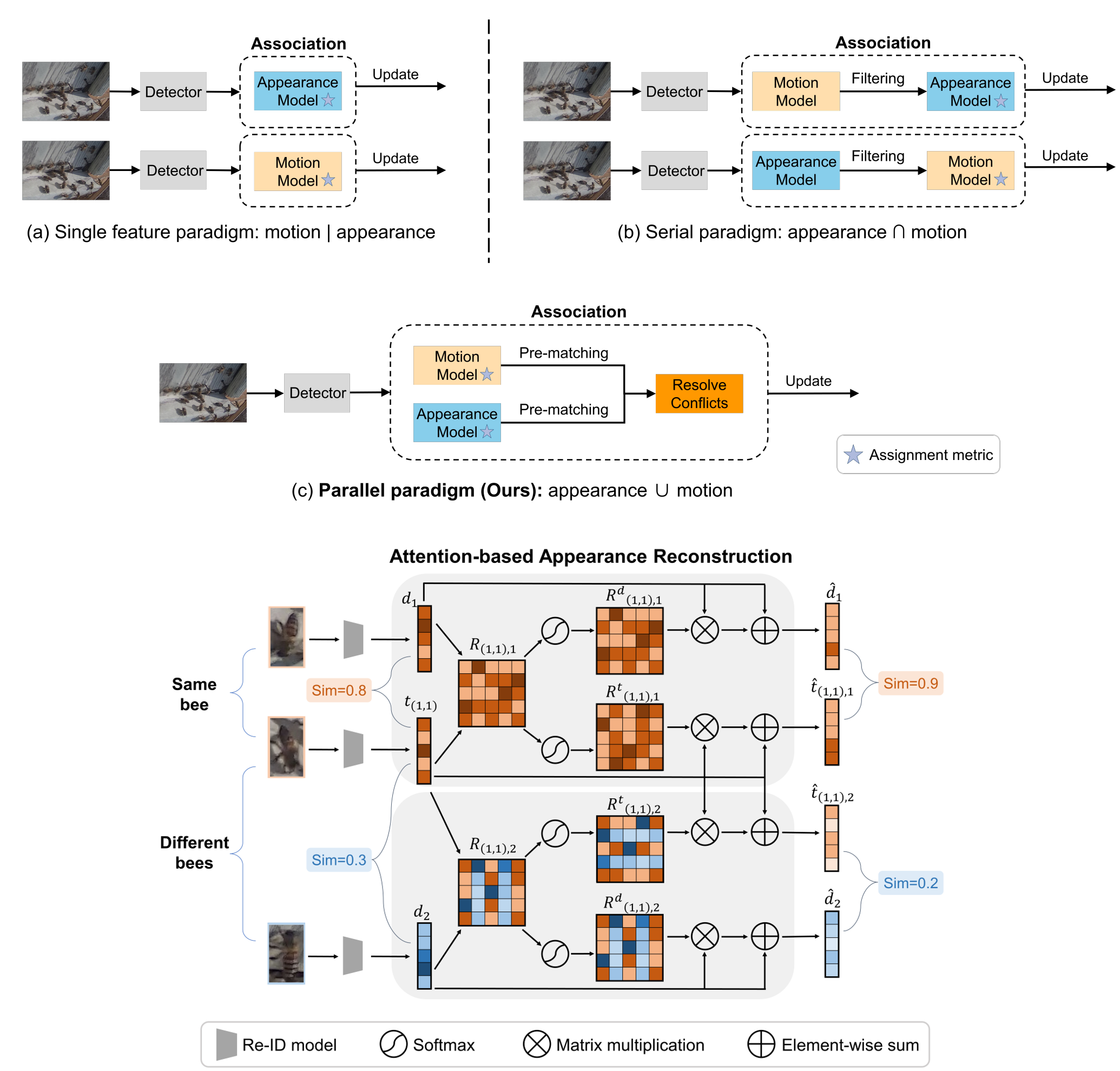

TOPIC: a parallel association paradigm for multi-object tracking under complex motions and diverse scenes
Xiaoyan Cao†, Yiyao Zheng†, Yao Yao†, Huapeng Qin, Xiaoyu Cao, Shihui Guo*(*corresponding author, †equal contribution)
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing (IEEE TIP) 2025 SCI Q1
We propose a parallel paradigm and present the Two rOund Parallel matchIng meChanism (TOPIC) to implement it. The TOPIC leverages both motion and appearance features and can adaptively select the preferable one as the assignment metric based on motion level. Moreover, we provide an Attention-based Appearance Reconstruction Module (AARM) to reconstruct appearance feature embeddings, thus enhancing the representation of appearance features.



Intelligent beehive monitoring system based on internet of things and colony state analysis
Yiyao Zheng, Xiaoyan Cao*, Shaocong Xu, Shihui Guo,, Rencai Huang, Yingjiao Li, Yijie Chen, Liulin Yang, Xiaoyu Cao, Zainura Idrus, Hongting Sun(*corresponding author, †equal contribution)
Smart Agricultural Technology 2024 SCI Q2
We proposed a hive monitoring system, and build a visualization module in the cloud to monitor the activity of bee colonies and the environmental dynamic changes. (1) We proposed a multi-bee tracking algorithm to solve the problem of monitoring bees at the door of the hive; (2) we constructed a dataset containing various complex scenes, named BEE22, for training and testing the performance of our algorithm; (3) we designed a bee counting rule, based on results of multi-bee tracking algorithm, to reasonably count the bees entering or leaving the beehive; (4) we have deployed multiple sensors around(center, margin, door, and environment) the hive to accurately reflect the changes in the environment around the hive.


High temporal resolution urban flood prediction using attention-based LSTM models
Lin Zhang, Huapeng Qin*, Junqi Mao, Xiaoyan Cao, Guangtao Fu(*corresponding author, †equal contribution)
Journal of Hydrology 2023 SCI Q1
This study proposes an attention mechanism-based Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network, named as ALSTM-DW, which uses double time sliding windows (DTSW), and a weighted mean square error (WMSE) loss function. The ALSTM-DW model was applied to three urban flooding hotspots in Shenzhen, China, and its effectiveness was verified through a series of comparative experiments.

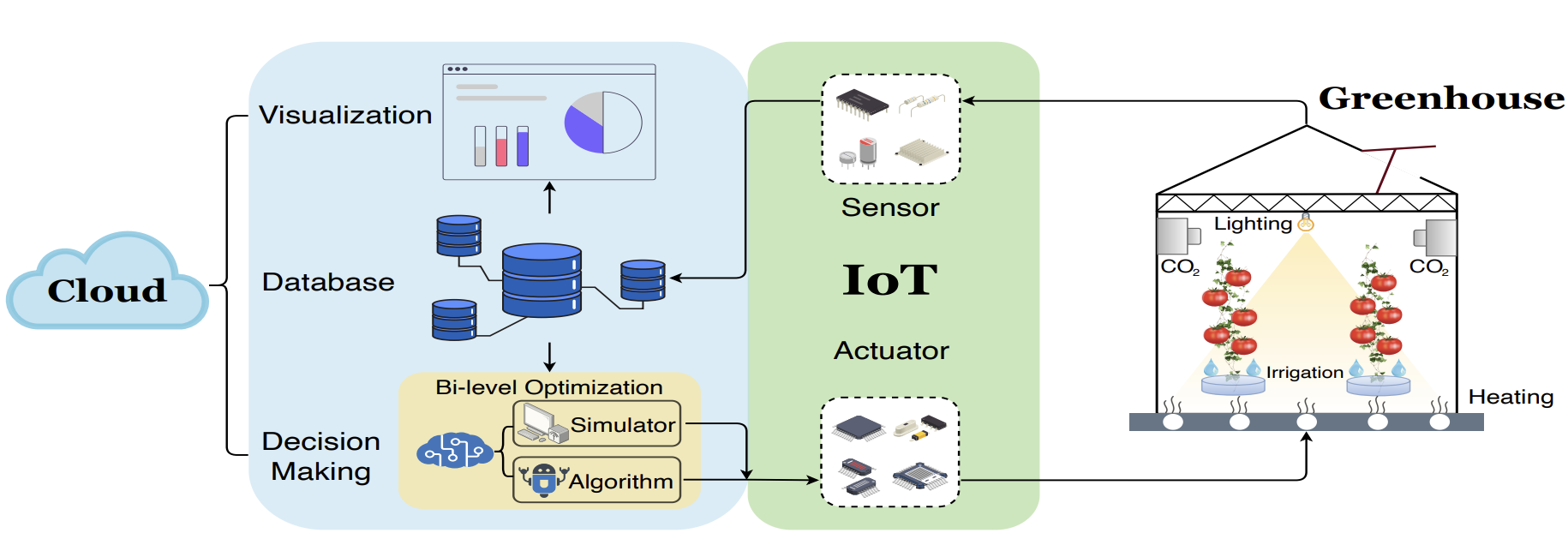
iGrow: a smart agriculture solution to autonomous greenhouse control
Xiaoyan Cao†, Yao Yao†, Lanqing Li, Wanpeng Zhang, Zhicheng An, Zhong Zhang, Li Xiao, Shihui Guo, Xiaoyu Cao, Meihong Wu, Dijun Luo*(*corresponding author, †equal contribution)
The Thirty-Sixth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-22) 2022 CCF-A
We propose a smart agriculture solution named iGrow, for autonomous greenhouse control (AGC): (1) for the frst time, we formulate the AGC problem as a Markov decision process (MDP) optimization problem; (2) we design a neural network-based simulator incorporated with the incremental mechanism to simulate the complete planting process of an autonomous greenhouse, which provides a testbed for the optimization of control strategies; (3) we propose a closed-loop bi-level optimization algorithm, which can dynamically re-optimize the greenhouse control strategy with newly observed data during real-world production. We not only conduct simulation experiments but also deploy iGrow in real scenarios, and experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of iGrow in autonomous greenhouse simulation and optimal control.

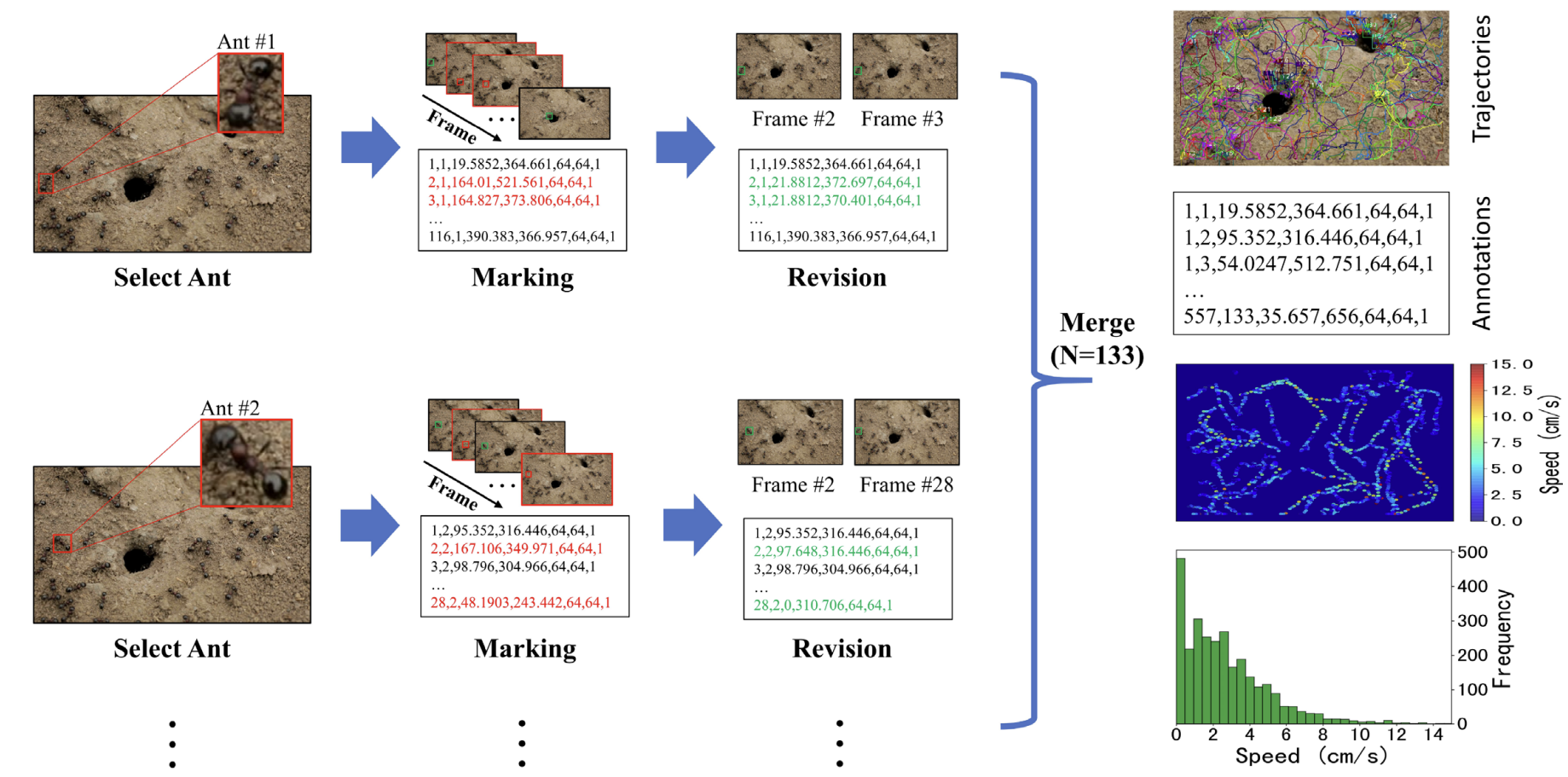
A dataset of ant colonies’ motion trajectories in indoor and outdoor scenes to study clustering behavior
Meihong Wu†, Xiaoyan Cao†, Ming Yang, Xiaoyu Cao, Shihui Guo*(*corresponding author, †equal contribution)
GigaScience 2022 SCI Q2
We collect 10 videos of 3 species of ant colonies from different scenes, including 5 indoor and 5 outdoor scenes. We develop an image sequence marking software named VisualMarkData, which enables us to provide annotations of the ants in the videos. (i) It offers comprehensive annotations of states at the individual-target and colony-target levels. (ii) It provides a simple matrix format to represent multiple targets and multiple groups of annotations (along with their IDs and behavior labels). (iii) During the annotation process, we propose a simple and effective visualization that takes the annotation information of the previous frame as a reference, and then a user can simply click on the center point of each target to complete the annotation task. (iv) We develop a user-friendly window-based GUI to minimize labor and maximize annotation quality.


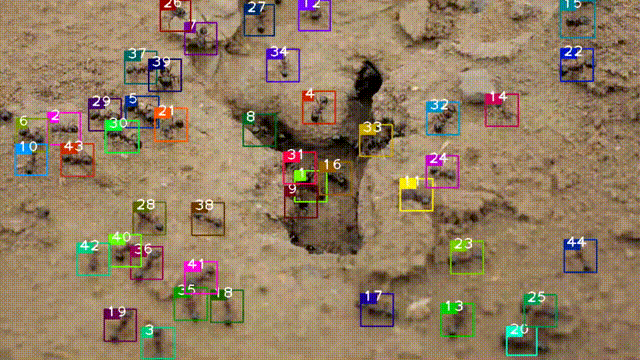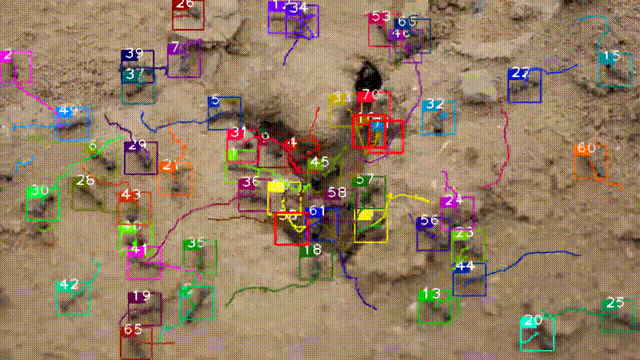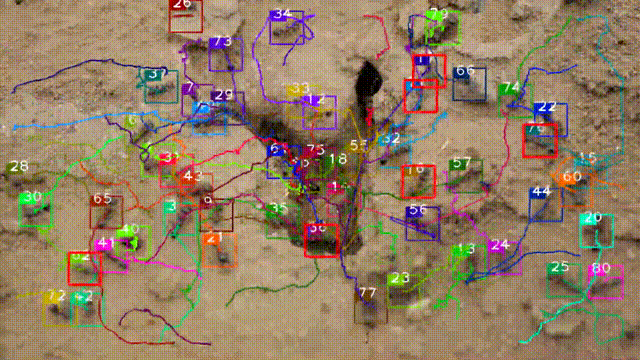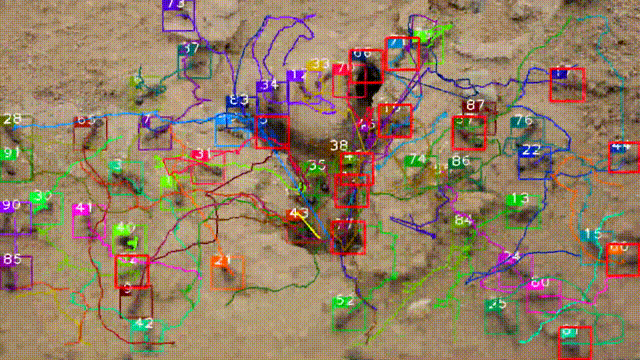
Swarm behavior tracking based on a deep vision algorithm
Meihong Wu, Xiaoyan Cao, Shihui Guo*(*corresponding author, †equal contribution)
Arxiv 2022 Preprint
We propose a detection and tracking framework for multi-ant tracking in the videos by: (1) adopting a two-stage object detection framework using ResNet-50 as backbone and coding the position of regions of interest to locate ants accurately; (2) using the ResNet model to develop the appearance descriptors of ants; (3) constructing long-term appearance sequences and combining them with motion information to achieve online tracking.



Robust Model-based Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous Greenhouse Control
Wanpeng Zhang, Xiaoyan Cao, Yao Yao, Zhicheng An, Xi Xiao, Dijun Luo*(*corresponding author, †equal contribution)
The 13th Asian Conference on Machine Learning (ACML 2021) 2021 CCF-C
we present a model-based robust RL framework for autonomous greenhouse control to meet the sample efficiency and safety challenges. Specifically, our framework introduces an ensemble of environment models to work as a simulator and assist in policy optimization, thereby addressing the low sample efficiency problem. As for the safety concern, we propose a sample dropout module to focus more on worst-case samples, which can help improve the adaptability of the greenhouse planting policy in extreme cases.


A simulator-based planning framework for optimizing autonomous greenhouse control strategy
Zhicheng An†, Xiaoyan Cao†, Yao Yao†, Wanpeng Zhang, Lanqing Li, Yue Wang, Shihui Guo, Dijun Luo*(*corresponding author, †equal contribution)
Proceedings of the Thirty-First International Conference on Automated Planning and Scheduling (ICAPS 2021) 2021 CCF-B
We propose a two-stage planning framework to automatically optimize greenhouse control setpoints given specific outside weather conditions. First, we take advantage of cumulative planting data and horticulture knowledge to build a multi-modular simulator, using neural networks to simulate climate change and crop growth in the greenhouse. Second, two AI algorithms (reinforcement learning and heuristic algorithm) are applied as planning methods to obtain optimal control strategies based on the simulator.

Online tracking of ants based on deep association metrics: method, dataset and evaluation
Xiaoyan Cao†, Shihui Guo†, Juncong Lin*, Wenshu Zhang, Minghong Liao(*corresponding author, †equal contribution)
Pattern Recognition 2020 SCI Q1
We introduce an online multi-object tracking framework that combines both the motion and appearance information of ants. We obtain the appearance descriptors by using the ResNet model for offline training on a small (N=50) sample dataset. For online association, a cosine similarity metric computes the matching degree between historical appearance sequences of the trajectory and the current detection.
